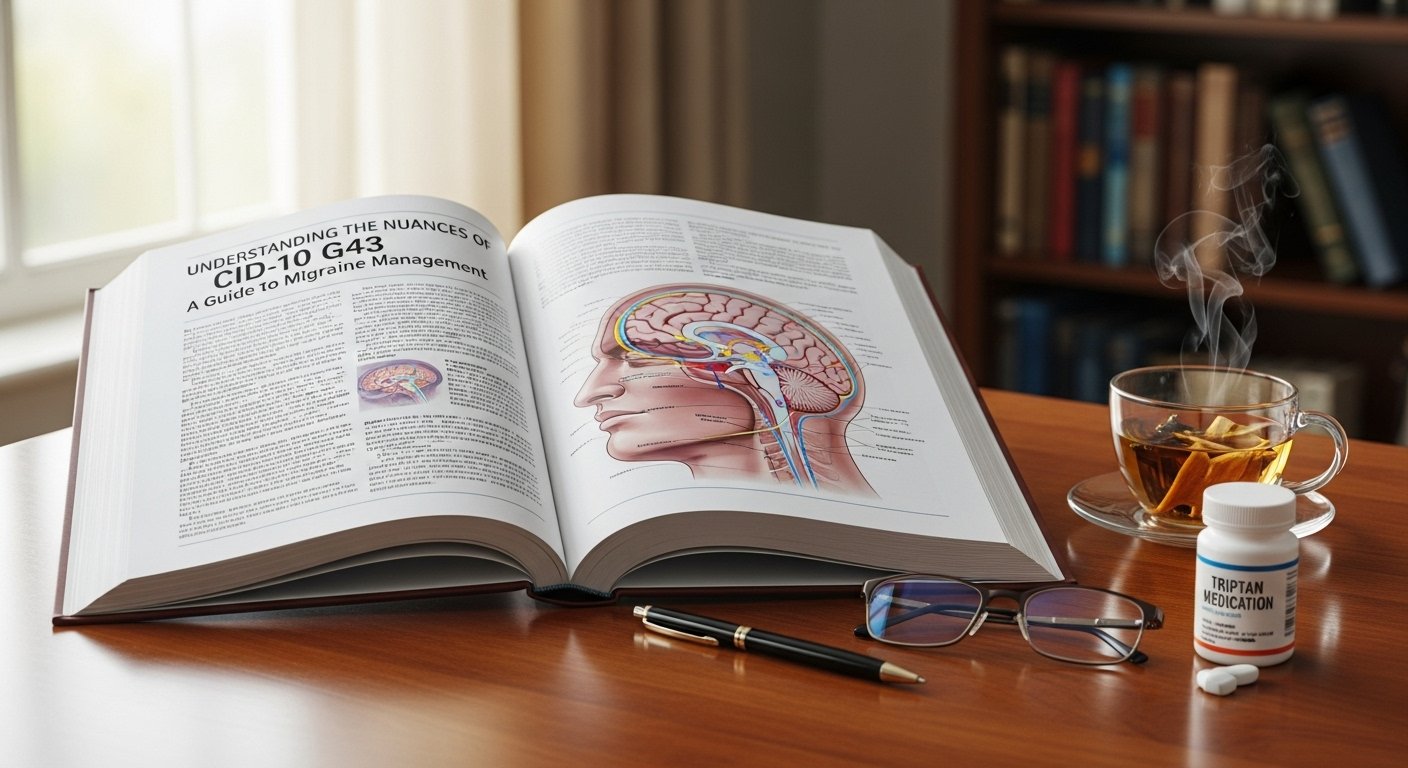
When it comes to neurological health, few conditions are as pervasive or as misunderstood as chronic headaches. Within the International Classification of Diseases, the code Cid10g43 serves as a vital diagnostic marker for migraine. While many people dismiss a migraine as “just a bad headache,” those living with the condition know it is a complex neurological syndrome that can be entirely debilitating. Navigating the world of medical coding and clinical symptoms is the first step toward regaining control over your quality of life.
Decoding the Diagnostic Framework
The medical community uses standardized codes to ensure that patients receive consistent care across different healthcare systems. When a physician mentions Cid10g43, they are specifically referring to the migraine family of disorders. This classification helps clinicians differentiate between tension-type headaches, cluster headaches, and the vascular or neurological shifts associated with migraines.
Using Cid10g43 allows for a more granular look at a patient’s history. It isn’t just about a label; it’s about the underlying pathophysiology. Migraines often involve cortical spreading depression and changes in the trigeminal nerve system. By categorizing a patient under Cid10g43, insurance providers and medical specialists can align on a treatment path that targets these specific biological mechanisms rather than offering a one-size-fits-all painkiller approach.
Identifying the Primary Symptoms
A diagnosis involving Cid10g43 typically requires the presence of specific criteria. Unlike standard headaches, migraines are often unilateral—affecting only one side of the head. The pain is usually described as throbbing or pulsating. However, the sensory disturbances are what truly set this condition apart.
Many individuals classified under Cid10g43 experience photophobia (sensitivity to light) and phonophobia (sensitivity to sound). In many cases, nausea and even vomiting accompany the physical pain. Some patients also experience an “aura,” which includes visual disturbances like flickering lights or blind spots. Recognizing these signs early is crucial because the sooner a Cid10g43 episode is identified, the more effectively it can be treated with abortive medications.
Common Triggers and Lifestyle Factors
Managing a condition labeled as Cid10g43 requires a bit of detective work. Triggers vary wildly from person to person. For some, it might be dietary—aged cheeses, nitrates in processed meats, or artificial sweeteners. For others, environmental factors like strong perfumes, flickering fluorescent lights, or sudden changes in barometric pressure can trigger a Cid10g43 event.
Stress management and sleep hygiene also play massive roles. Irregular sleep patterns are a notorious catalyst for those prone to Cid10g43. By maintaining a consistent “migraine diary,” patients can track their habits alongside their symptoms, eventually identifying patterns that lead to a Cid10g43 flare-up. Reducing these triggers doesn’t always eliminate the condition, but it significantly lowers the frequency and intensity of the attacks.
Modern Treatment Modalities
The landscape for treating Cid10g43 has evolved significantly over the last decade. We have moved beyond simple analgesics into the realm of triptans, which specifically target serotonin receptors to constrict blood vessels and block pain pathways in the brain. For those with chronic Cid10g43, preventive measures are often necessary.
Preventive treatments might include beta-blockers, anti-seizure medications, or even Botox injections, which have been FDA-approved for chronic migraine prophylaxis. More recently, CGRP (Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide) inhibitors have revolutionized the way we handle Cid10g43. These are designed to block a protein that carries pain signals during a migraine attack. Discussing these advanced options with a neurologist ensures that your Cid10g43 management plan is as modern and effective as possible.
The Importance of Professional Consultation
Self-diagnosis can be dangerous when dealing with neurological symptoms. While the Cid10g43 code provides a framework, other underlying issues must be ruled out by a professional. If your headaches are accompanied by sudden weakness, confusion, or a fever, it is imperative to seek immediate help rather than assuming it is a standard Cid10g43 episode.
A dedicated specialist will use the Cid10g43 designation to monitor your progress over time. They will look at the “burden of disease”—how much the condition interferes with your work, social life, and mental well-being. By treating Cid10g43 as a legitimate, chronic neurological condition, the medical community can offer the support and empathy that patients truly deserve.
Conclusion
Living with a diagnosis of Cid10g43 is undeniably challenging, but it is not a journey you have to take alone. Through a combination of accurate diagnostic coding, trigger identification, and modern pharmacological interventions, most people can find significant relief. Understanding that Cid10g43 represents a specific biological event rather than a phantom pain is the first step toward effective advocacy for your own health. With the right tools and professional guidance, the days lost to dark rooms and intense pain can become a thing of the past.